Pierre Mahé

PhD in computer science and signal processing from University of La Rochelle, France.
| Home |
| Publications |
| Perso |
| CV |
| Contact |
Conferences
Ambisonic Coding with Spatial Image Correction
Pierre Mahé, Stéphane Ragot, Sylvain Marchand and Jérôme Daniel
EUSIPCO, 2021, January 18-22, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Paper / Video presentation / Slides
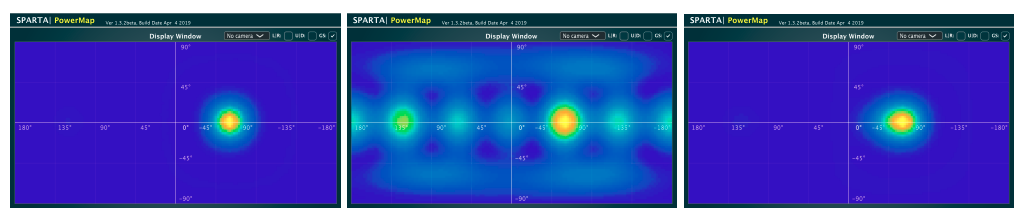
We present a new method to enhance multi-mono coding of ambisonic audio signals. In multi-mono coding, each component is represented independently by a mono core codec, this may introduce strong spatial artifacts. The proposed method is based on the correction of spatial images derived from the sound-field power map of original and coded ambisonic signals. The correction metadata is transmitted as side information to restore the spatial image by post-processing. The performance of the proposed method is compared against naive multi-mono coding (with no side information) at the same overall bitrate. Experimental results are provided for the case of First-Order Ambisonic (FOA) signals and two mono core codecs: EVS and Opus. The proposed method is shown to provide on average some audio quality improvement for both core codecs. ANOVA results are provided as a complementary analysis.
First-Order Ambisonic Coding with PCA Matrixing and Quaternion-Based Interpolation
Pierre Mahé, Stéphane Ragot and Sylvain Marchand
EAA Spatial Audio Signal Processing Sympasium, 2019, September 6-7, Paris, France
Paper / Slides
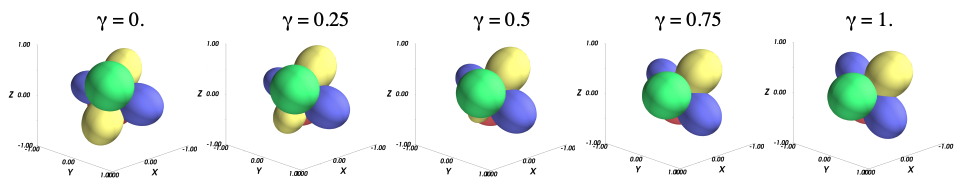
We present a new first-order ambisonic (FOA) coding method extending existing speech/audio codecs such as EVS or Opus. The proposed method is based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and multi-mono coding with adaptive bit allocation. The PCA operating in time-domain is interpreted as adaptive beamforming. To guarantee signal continuity between frames, beamforming matrices are interpolated in quaternion domain. The performance of the proposed method is compared with naive multi-mono coding with fixed bit allocation. Results show significant quality improvements at bit rates from 52.8 kbit/s (4 × 13.2) to 97.6 kbit/s (4 × 24.4) using the EVS codec.
First-Order Ambisonic Coding with PCA Matrixing and Quaternion-Based Interpolation
Pierre Mahé, Stéphane Ragot and Sylvain Marchand
DAFx, 2019, September 2-6, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Paper / Slides
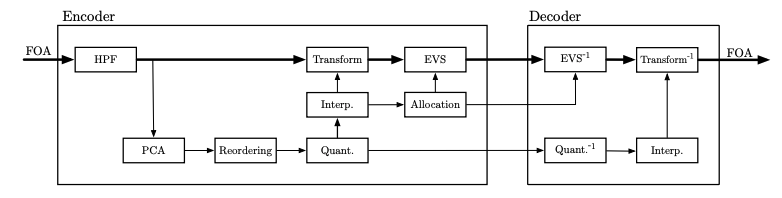
We present a spatial audio coding method which can extend existing speech/audio codecs, such as EVS or Opus, to represent first-order ambisonic (FOA) signals at low bit rates. The proposed method is based on principal component analysis (PCA) to decorrelate ambisonic components prior to multi-mono coding. The PCA rotation matrices are quantized in the generalized Euler angle domain; they are interpolated in quaternion domain to avoid discontinuities between successive signal blocks. We also describe an adaptive bit allocation algorithm for an optimized multi-mono coding of principal components. A subjective evaluation using the MUSHRA methodology is presented to compare the performance of the proposed method with naive multi-mono coding using a fixed bit allocation. Results show significant quality improvements at bit rates in the range of 52.8 kbit/s (4 × 13.2) to 97.6 kbit/s (4 × 24.4) using the EVS codec.
Posters and Presentations
My 3 Minutes Thesis presentation
Pierre Mahé
JJCAAS, 2019, June 27-28, Le Mans, France
Live recording
Codage Ambisonique pour les Communications Immersives
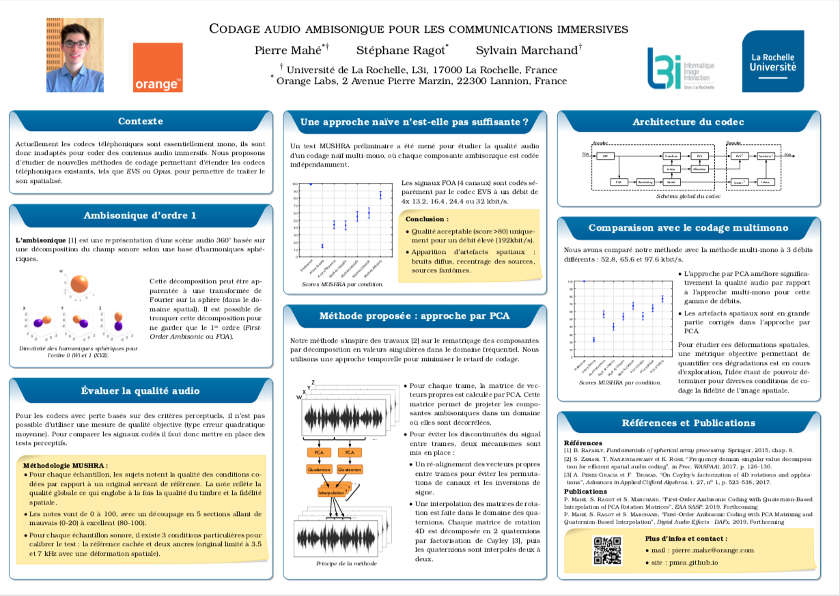
Pierre Mahé, Stéphane Ragot and Sylvain Marchand
JJCAAS, 2019, June 27-28, Le Mans, France
Poster